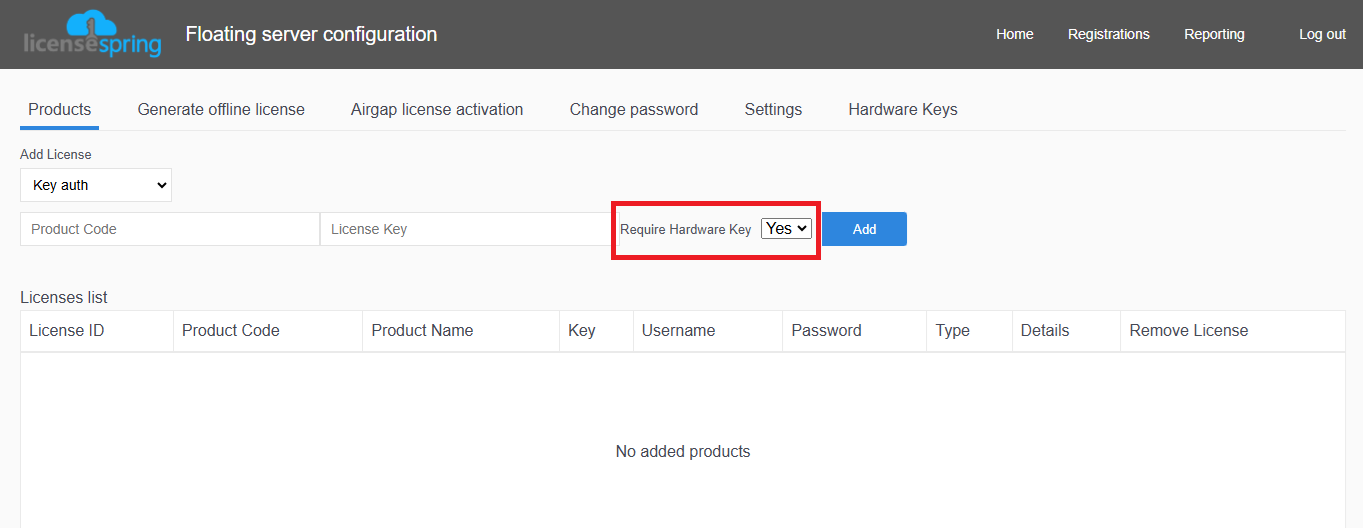
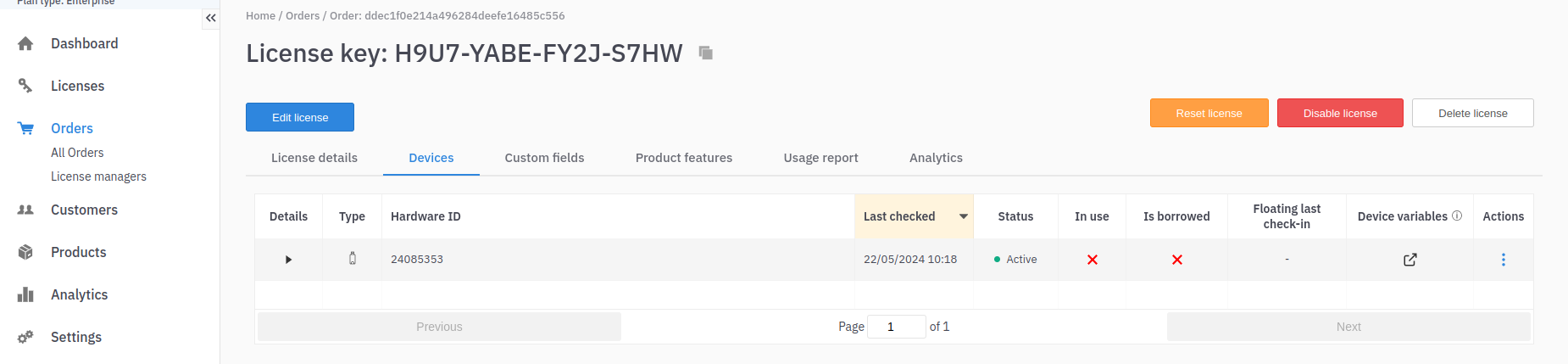
Hardware Key
In the floating server, when the hardware key is plugged in and a license-requiring hardware key is added to the floating server, the server's hardware ID changes to the serial number of the hardware key. From then on, every other action in this server uses the new hardware ID, as long as the hardware key is connected to the server. Multiple licenses can be activated using the same hardware key.
To successfully run the floating server with the hardware dongle, make sure that no other process is using smart card readers, as this will result in an error in the floating server.
More details on how to detect those services can be found at the end of this page.
Activate a hardware-key-requiring license
The following steps are required to activate a hardware-key-requiring license in the floating server:
Create a Hardware-Key-Requiring License
Follow Hardware Key Licensing to create a license that requires a hardware key.
Once a hardware-key-based license is added to the server, any subsequent actions involving that license will first verify the hardware key's validity. The action will fail if the key is invalid (e.g., disconnected).
Invalid Hardware Key Handling
To address scenarios with missing or invalid hardware keys, we provide two solutions:
Default Behavior: When a hardware key is missing or invalid, the server returns an error.
Crash on Missing Hardware Key: If the
crashIfNoHardwareKeyflag is set to true during server setup, the server will crash when an invalid or missing hardware key is accessed.
This feature was introduced in version v1.6.0 and was implemented to accommodate specific use cases, such as managing hardware keys in high-availability setups.
Usage examples
Using the API to log in as an admin, add consumptions, feature consumptions, register a user, and register a user to a feature of a license that requires hardware key verification. This example takes advantage of authentication mode to enforce role-based access control. If you are using the server without authentication mode, you can omit the authorization headers.
Use user/pass to login
curl -u 'user1':'pass1' http://localhost:8080/auth -H "Accept: application/json"Response:
{"message":"Login successful","token":"eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJleHAiOjE3MjY4NTU4OTMsImlhdCI6MTcyNjc2OTQ5Mywicm9sZSI6ImFkbWluIiwidXNlcm5hbWUiOiJ1c2VyMSJ9.fhJefnu7X7iECS3Brf36PVdqHRLeZIuwONTfkHdJnjA"}
Add the product
using the "isHWKeyReq" parameter
Add consumptions
Add feature consumptions
Register User
If no errors occur, the license object will be returned.
Register User to Feature
Response: {"product":"hwbased","feature":"consFeature2","user":"user2","os_hostname":"","ip_local":"0.1.1.1","user_info":"","registered_at":"2024-09-19T12:39:16.356495803-07:00","borrowed_until":"0001-01-01T00:00:00Z"}
Unplug the hardware key or restart the server, then add consumption
Response: {"code":"hardware_key_not_accessible","message":"No available valid hardware key to perform the action: adding feature consumption","status":400}
Detect processes using smart card reader
To find which processes are using a smart card reader on your machine, you can use the following methods depending on your operating system:
On Linux
Use
lsof: Thelsofcommand lists open files and the processes that have opened them. Since smart card readers are typically handled as devices, you can find processes interacting with them.First, find the device file for your smart card reader. This is usually in
/devand might be something like/dev/pcsc,/dev/ttyUSB0, or similar.Run the following command to check which processes are accessing the device:
Example:
Check PC/SC Daemon: If you’re using a PC/SC compliant smart card reader, the
pcscdservice manages the communication. You can check ifpcscdis running, and find its process ID:
Use
fuser: Thefusercommand shows which processes are accessing a specific file or device:
On Windows
Use Task Manager: Open the Task Manager (Ctrl + Shift + Esc), and look for applications or services related to smart card access, like "Smart Card Service" or "SCardSvr". These may interact with the smart card reader.
Use
sc query: You can also use the command prompt to query the status of the Smart Card service:
Sysinternals Tools: The Sysinternals Process Explorer allows you to see what files, directories, and handles processes are using. Open Process Explorer and search for processes accessing smart card-related files or drivers.
On macOS
Use
lsof: Similar to Linux, you can uselsofto find processes using the smart card reader:
Check the Smart Card Daemon: On macOS, the
pcsctestcommand can interact with the smart card reader and might provide information about active processes:
These methods should help you identify which processes are interacting with your smart card reader.
Last updated
Was this helpful?